News
Apple Watch Gets UAE Approval For Sleep Apnea Detection
The UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention has given the green light to the feature which monitors interruptions in breathing patterns.
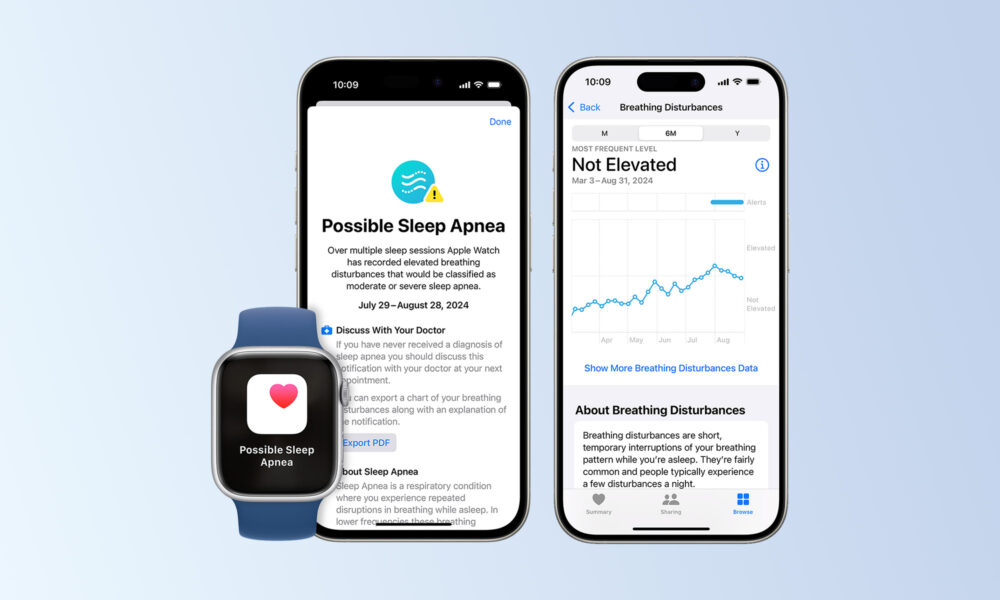
Apple Watch users in the United Arab Emirates now have access to a new health feature designed to detect potential signs of moderate to severe sleep apnea after Apple secured marketing authorization from the UAE Ministry of Health and Prevention.
Sleep apnea is a serious condition where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep, and often remains undiagnosed. Affecting an estimated one billion people globally, if untreated, sleep apnea can lead to health complications, including hypertension, Type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular issues.
This new detection feature utilizes the Apple Watch’s accelerometer to monitor wrist movements associated with interruptions in breathing. These “Breathing Disturbances” are analyzed by a specific Apple Watch metric, allowing users to view data in the Health app on their iPhone or iPad.
While occasional disturbances are normal, Apple’s monitoring focuses on patterns that occur frequently over multiple nights, as they may indicate sleep apnea. The app classifies breathing patterns as either elevated or not elevated, and users can track their breathing disturbance history over one-month, six-month, or one-year periods.
Also Read: How To Clean Your Apple Watch Like A Pro
Every 30 days, Apple’s system analyzes the accumulated data for signs of moderate to severe sleep apnea. If it identifies consistent patterns, the user receives a notification advising them to consult a healthcare provider. The notification includes an educational section about sleep apnea risks, as well as a PDF summary containing three months of relevant data, which users can share with their doctors for further discussion.
The Sleep Apnea Notification algorithm was developed with advanced machine learning and a large dataset of clinical sleep apnea studies. Apple validated the feature in an extensive clinical trial, one of the largest conducted for sleep apnea detection technology. In this study, each participant identified by the algorithm as having a breathing disturbance showed at least mild sleep apnea.