News
UAE To Unleash Hordes Of Cloud-Triggering Drones

The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a massive problem with a limited supply of rainwater. With an average rainfall of just 100 mm per year, the constitutional monarchy is ranked among the most water-stressed countries in the world.
For years now, the country’s government has been investing heavily in various cloud-seeding missions aimed to increase the annual rainfall. For example, the UAE has been relatively successfully triggering rain by firing salt particles into clouds from airplanes to make individual water particles heavier and more likely to punch holes in the clouds.
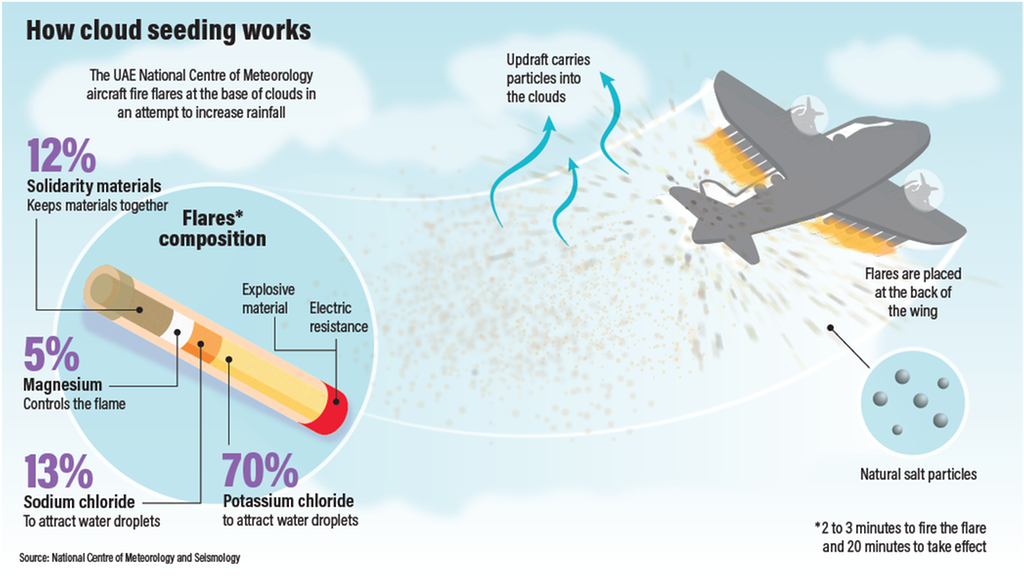
National Centre Of Meteorology & Seismology
Now, UAE scientists have partnered with their colleagues from the University of Reading, England, to make it rain more in the parched country by literary giving clouds electric shocks.
“Equipped with a payload of electric charge-emitting instruments and custom sensors, these drones will fly at low altitudes and provide an electric charge to air molecules, which should stimulate precipitation,” explains Alya Al-Mazroui, the Director of the UAE Research Program for Rain Enhancement Science.
By deploying an electric current with negative and positive ions, the drones will basically attempt to recreate the natural phenomenon that causes dry hair to be attracted to a plastic comb. Since particles with opposite charges attract each other, the electricity unleashing drones should theoretically cause small droplets of water to merge into more subscription cloud formations and eventually lead to rain.
Also Read: Amazon Is Planning To Create Over 1,500 Jobs In Saudi Arabia
“Our project aims to evaluate the importance of charge in affecting the cloud droplet size distribution and rainfall generation through modifying the behavior of droplets and particles and studying the microphysical and electric properties of fog events,” says Professor Giles Harrison, a Professor of Atmospheric Physics in the Department of Meteorology at the University of Reading.
The effectiveness and safety of various cloud-seeding practices, including those explored by the UAE, are still debated by scientists. Concerns have been raised about their geopolitical implications, with wealthy, technologically advanced countries potentially “stealing” rainwater that would otherwise naturally end up in poorer countries.