News
Japan Sets New Record For Data Transmission Speed
The researchers have absolutely smashed their own previous achievement by transmitting data at a jaw-dropping 1.02 petabits per second.
A team of researchers from the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) in Japan is at it again. After achieving a data transmission speed of 319 terabits per second (Tb/s) last year, the researchers have now absolutely smashed their own previous achievement by transmitting data at 1.02 petabits per second (Pb/s).
Since 1 petabits is 125,000 gigabytes, it means that the team could theoretically transmit more than 31,000 movies in 4K resolution every single second. To make the record even more impressive, it’s important to highlight that it was achieved using fiber-optic cables with four cores, which is exactly how many cores were used to set the previous record.
“NICT constructed the transmission system using 4-core MCF with standard 0.125 mm cladding diameter, WDM technology and mixed optical amplification systems. The system allowed a data transmission speed of 1.02 petabit per second over 51.7 km,” explained the researchers in the official press release.
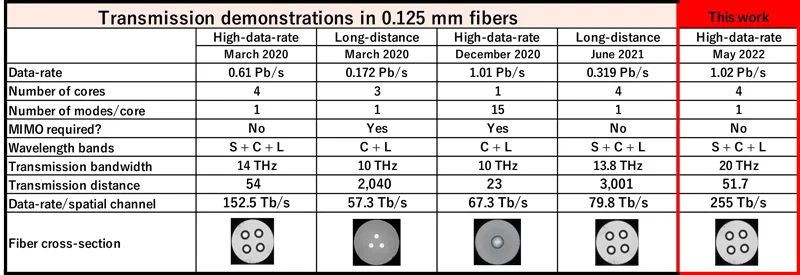
The mind-blowing record was first presented in May at the International Conference on Laser and Electro-Optics (CLEO) 2022 in San Jose, California, one of the largest international conferences related to optical devices and systems.
Also Read: Microsoft Blocks Lebanon-Based Hackers Targeting Israel
Moving forward, the NICT team wants to continue exploring different ways to transmit data faster across fiber optic cables. Their main focus is on low-core-count multi-core fibers with standard cladding diameter because such cables are comparable to standard single-mode fibers and thus more attractive for early adoption.
With dozens of countries around the world actively moving from 4G to 5G broadband cellular networks, the massive amount of data being sent and received is guaranteed to continue increasing at a rapid pace. Research projects such as the one behind the latest record can pave the way for new fibers capable of meeting the growing demand and supporting new bandwidth-hungry services.