News
100K+ Compromised ChatGPT Accounts Found On Dark Web
Egypt, Morocco, and Algeria top the list in the Middle Eastern region.

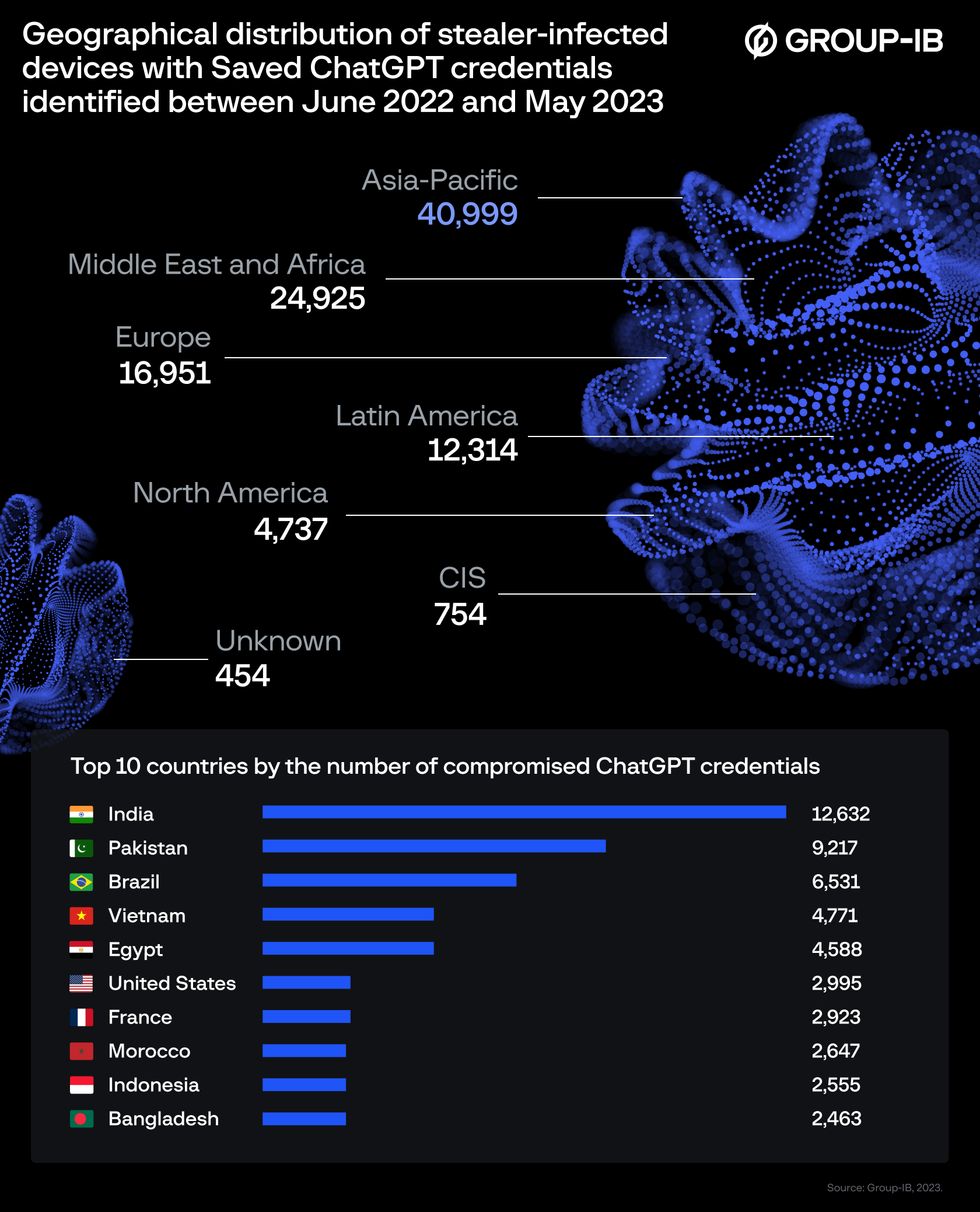
Global cybersecurity leader Group-IB has identified 101,134 infected devices with saved ChatGPT credentials. Throughout 2023, the company’s Threat Intelligence Platform found compromised account details in 26,802 malware logs traded on dark web marketplaces.
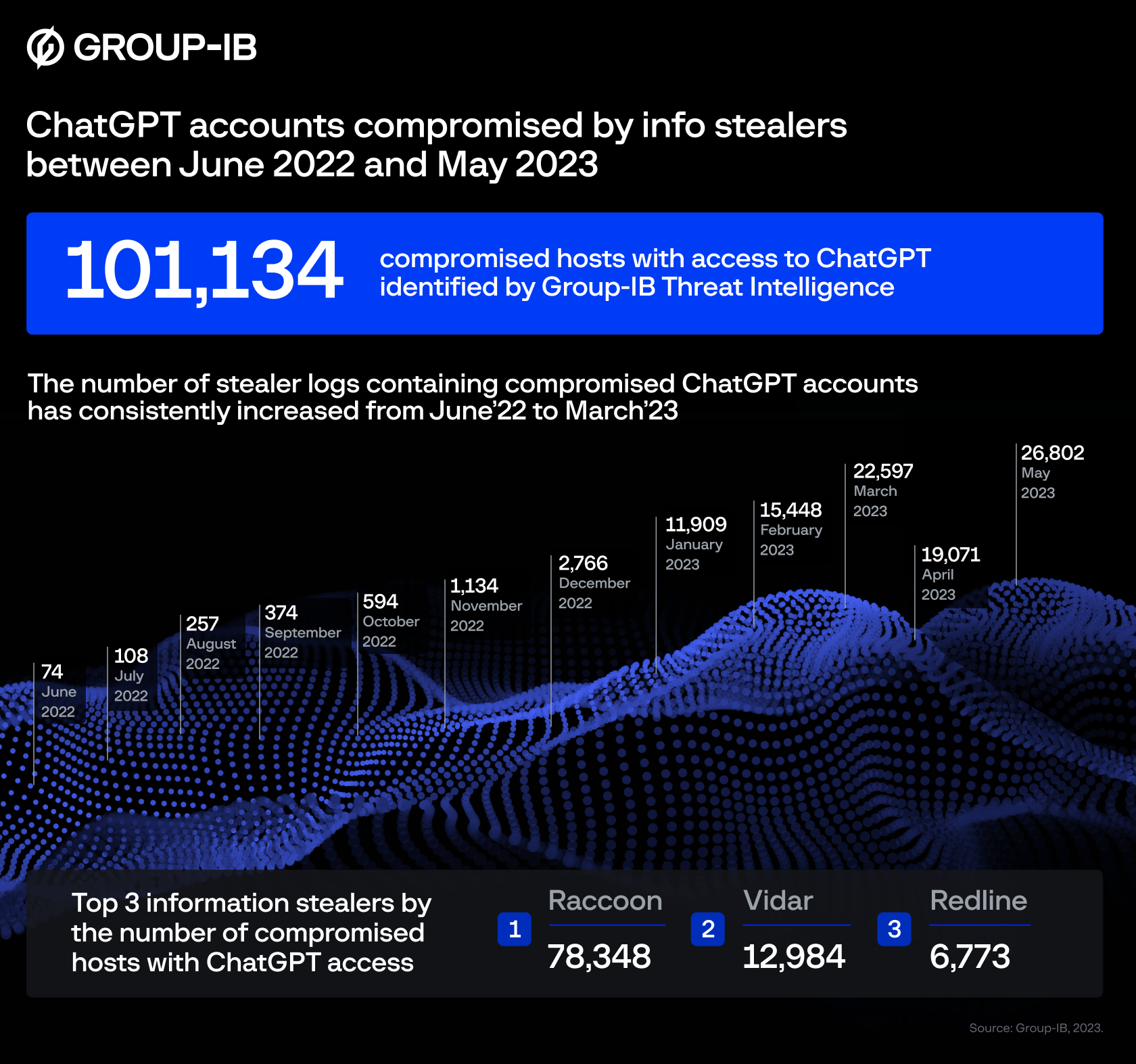
According to Group-IB’s findings, the Asia-Pacific region suffered the greatest concentration of ChatGPT credentials offered for sale, followed by the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region in second place.
Group-IB tech experts explained that when employees take advantage of ChatGPT to optimize business communications and marketing texts, the queries and responses are stored within the AI app. Consequently, any unauthorized access to a ChatGPT account could unearth a wealth of sensitive information.
Also Read: The Largest Data Breaches In The Middle East
Group-IB’s dark web analysis revealed that most compromised ChatGPT accounts were breached by a popular malware program known as “Raccoon Info Stealer”. The virus is often sent by email and can be used by hackers to gain access to sensitive data stored in internet browsers.
In the MENA area, accounts from users in Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, and Turkey topped the “most-infected” list, potentially exposing companies in the region to multiple threat actors.
“Many enterprises are integrating ChatGPT into their operational flow,” explained Dmitry Shestakov, Head of Threat Intelligence at Group-IB. “Employees enter classified correspondences or use the bot to optimize proprietary code. Given that ChatGPT’s standard configuration retains all conversations, this could inadvertently offer a trove of sensitive intelligence to threat actors if they obtain account credentials. At Group-IB, we continuously monitor underground communities to identify such accounts promptly”.
To mitigate the risks posed by compromised ChatGPT accounts, Group-IB suggests that users update passwords using current best practices while also implementing two-factor authentication.
News
Mamo Completes $3.4M Funding Round To Enhance Fintech Services
The startup will use the influx of cash to expand into Saudi Arabia and across the wider GCC while improving its product offering.

UAE-based fintech Mamo has announced the completion of a $3.4 million funding round that will help the startup extend its market presence and improve its product offering. Investors included 4DX Ventures, the Dubai Future District Fund and Cyfr Capital.
Mamo’s platform offers “payment collection, corporate cards and expense management” to help small and medium-sized businesses consolidate and streamline their operations. With the latest influx of capital, Mamo will further develop its comprehensive suite of services and begin testing its product lines in Saudi Arabia, further extending its footprint across the GCC.
Imad Gharazeddine, co-founder and CEO of Mamo, stated: “We’ve been in the market for a while now and are incredibly proud of what our team has achieved. The holistic and expansive nature of our product offering has helped us continue to grow sustainably. This additional funding will allow us to reach our medium-term goals even faster. The support from new and existing investors is a testament to our strong expertise and the ability to deliver on our customer promise”.
Daniel Marlo, General Partner of lead investor 4DX Ventures, added: “We have immense trust in Imad’s vision, leadership and Mamo’s innovative approach to provide a user-friendly and comprehensive financial solution for SMEs that makes financial management more accessible and efficient. We are proud to partner with them and support their mission”.
Also Read: A Guide To Digital Payment Methods In The Middle East
Amer Fatayer, Managing Director of Dubai Future District Fund’s investment team, also commented: “Mamo’s localized product lines serve as an infrastructure for SME payments and spend management in UAE, a segment that is underserved by the country’s current banking infrastructure. The team has taken a product-first approach to consolidating SMEs’ financial journeys and building a fintech solution deeply embedded in a business’s core operations”.
To date, Mamo has raised around $13 million in investment funding and now boasts a team of 30 people. The company’s intuitive financial services platform has allowed over 1,000 businesses to consolidate their financial operations and significantly reduce payment fees.
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoAmazon Prime Day 2024: Get Ready For 6 Days Of Amazing Deals
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoSamsung Unpacked 2024: What To Expect From The July 10 Event
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoCoursera Report Shows Surge In UAE Interest In AI Upskilling
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMeet Dubai’s Groundbreaking Smart Robot Delivery Assistant