News
Google Is Developing An AI Cancer-Spotting Microscope
The search giant has teamed up with the US Department of Defense to build the new detection tool.
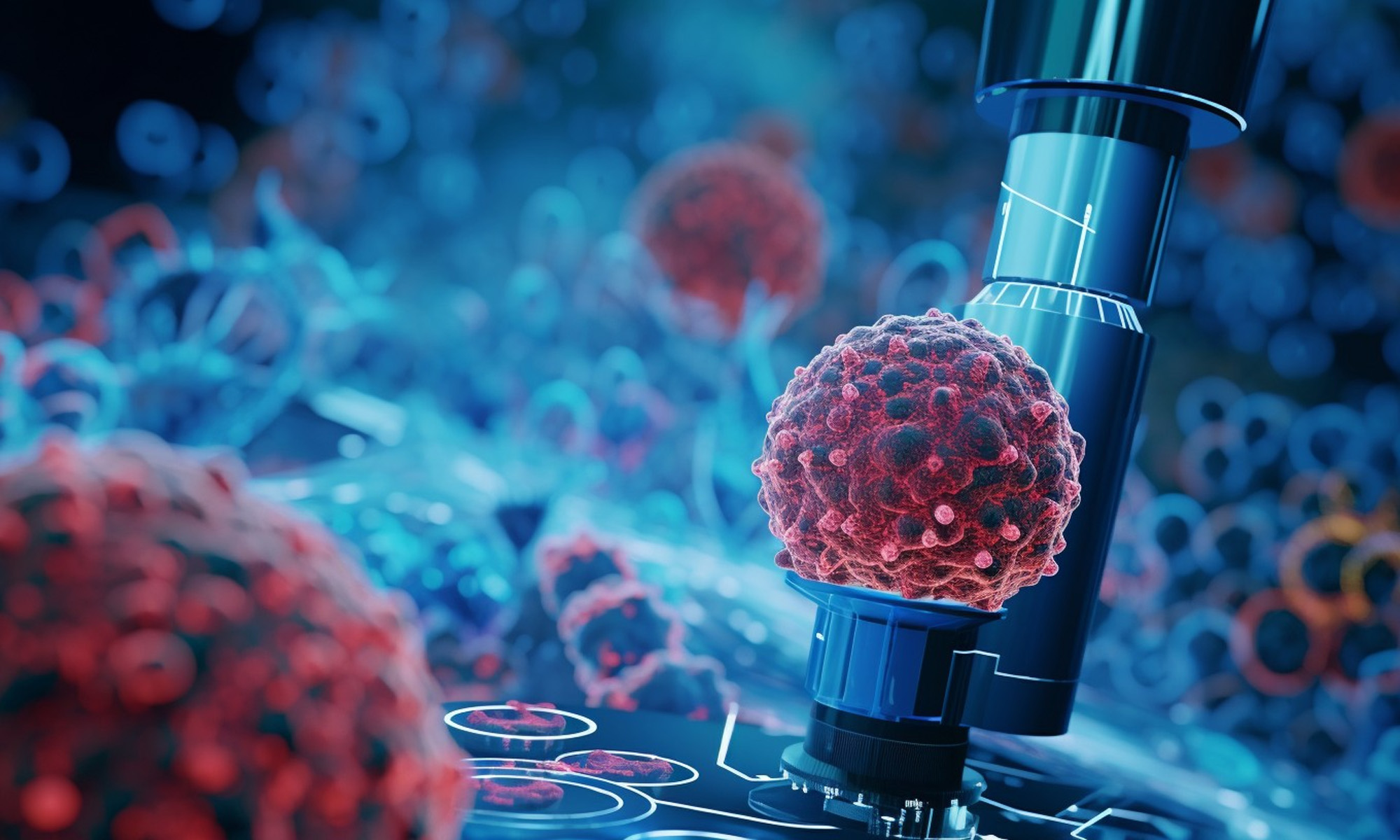
Google has developed an “Augmented Reality Microscope” (ARM) in collaboration with the US Department of Defense. The prototype uses AI enhancements to add real-time visual indicators such as heat maps or object boundaries, making identifying the presence of known pathogens and cancer cells easier.
The ARM was first teased in 2018, and the latest prototype has still not been used to diagnose real patients. After further testing, Google hopes that the technology will be “retrofitted into existing light microscopes in hospitals and clinics”. Once installed, ARM-equipped microscopes will give clinicians a variety of visual feedback cues, including text, arrows, contours, animations and heat maps.
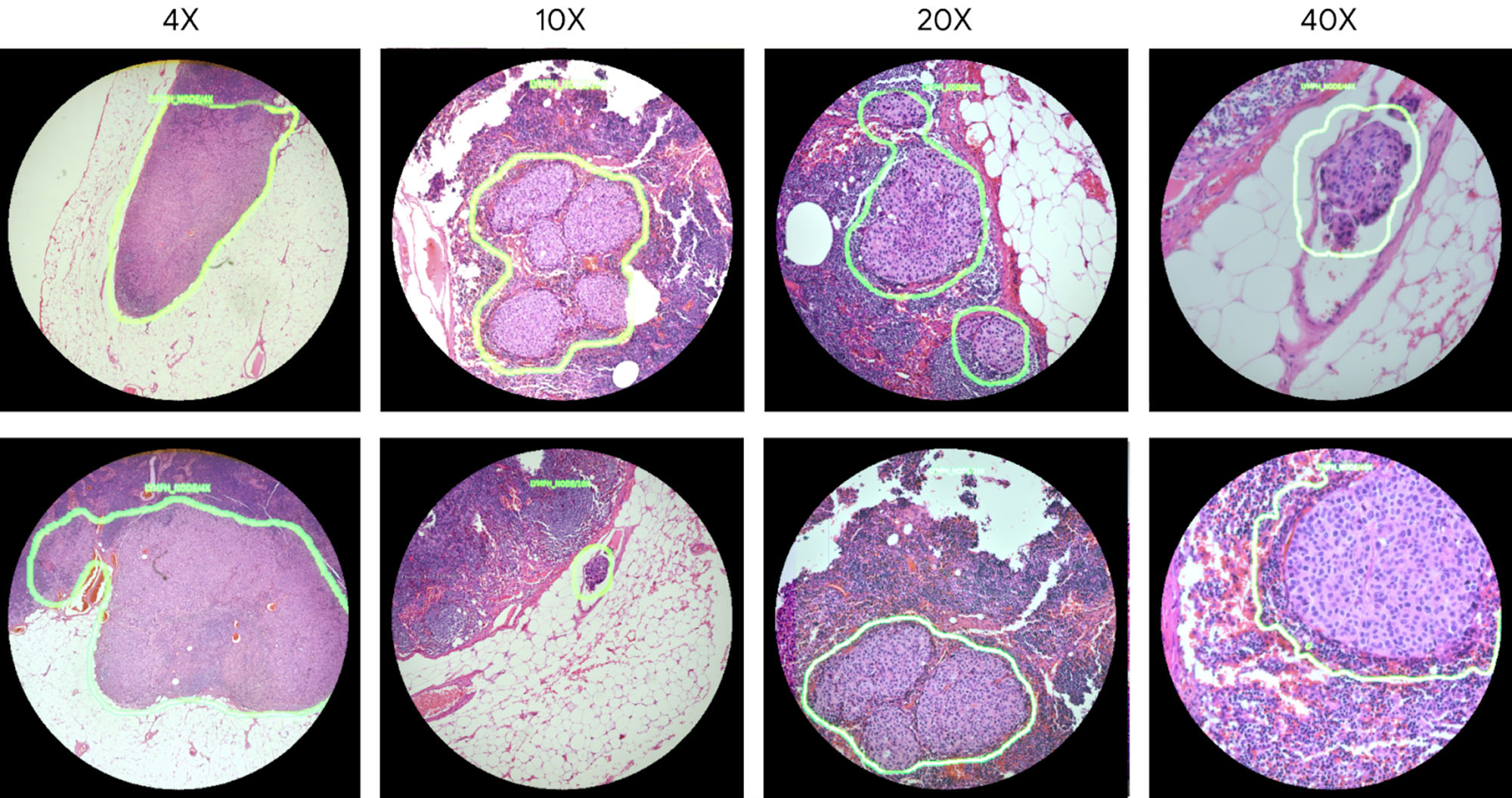
The US Department of Defense’s “Defense Innovation Unit” has already negotiated agreements with Google to enable Augmented Reality Microscope distribution through military channels. ARM is expected to cost $90,000 to $100,000 per unit — a figure well beyond many local health providers.
Also Read: Canadian University Dubai Students Create Smart Garbage Bin
This is not the first time Google Health has invested in AI-powered diagnostic tools. Parent company Alphabet already has a strong record of partnering with startups that invest in AI to “improve healthcare” and is projected to have spent over $200 billion on AI technology over the past decade — something that’s especially noteworthy at a time when the World Health Organization is predicting a worldwide deficit of 15 million health care workers by 2030.
News
Rabbit Expands Hyperlocal Delivery Service In Saudi Arabia
The e-commerce startup is aiming to tap into the Kingdom’s underdeveloped e-grocery sector with a tech-first, locally rooted strategy.
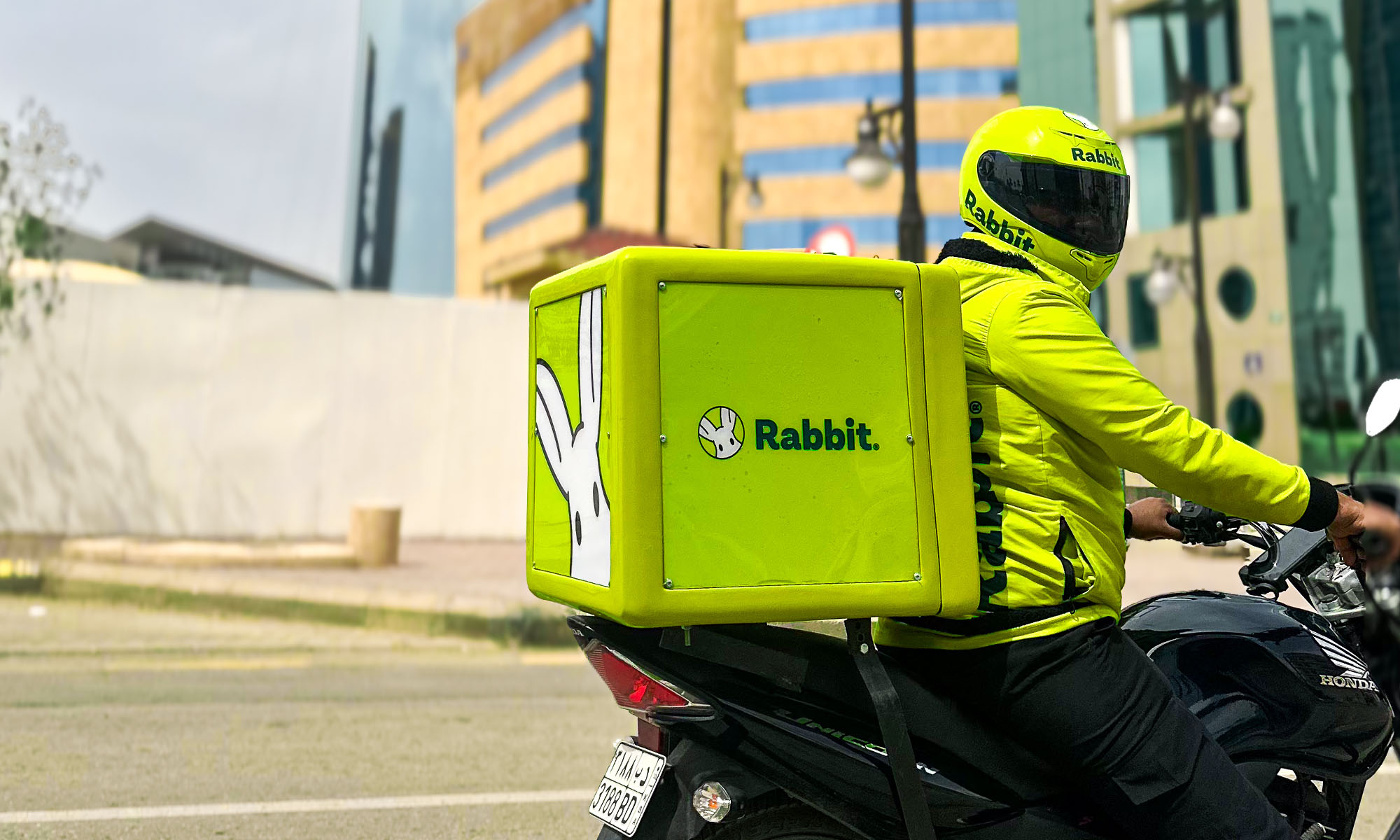

Rabbit, an Egyptian-born hyperlocal e-commerce startup, is expanding into the Saudi Arabian market, setting its sights on delivering 20 million items across major cities by 2026.
The company, founded in 2021, is already operational in the Kingdom, with its regional headquarters now open in Riyadh and an established network of strategically located fulfillment centers — commonly known as “dark stores” — across the capital.
The timing is strategic: Saudi Arabia’s online grocery transactions currently sit at 1.3%, notably behind the UAE (5.3%) and the United States (4.8%). With the Kingdom’s food and grocery market estimated at $60 billion, even a modest increase in online adoption could create a multi-billion-dollar opportunity.
Rabbit also sees a clear alignment between its business goals and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, which aims to boost retail sector innovation, support small and medium-sized enterprises, attract foreign investment, and develop a robust digital economy.
The company’s e-commerce model is based on speed and efficiency. Delivery of anything from groceries and snacks to cosmetics and household staples is promised in 20 minutes or less, facilitated by a tightly optimized logistics system — a crucial component in a sector where profit margins and delivery expectations are razor-thin.
Despite the challenges, Rabbit has already found its stride in Egypt. In just over three years, the app has been used by 1.4 million customers to deliver more than 40 million items. Revenue has surged, growing more than eightfold in the past two years alone.
Also Read: Top E-Commerce Websites In The Middle East In 2025
CEO and Co-Founder Ahmad Yousry commented: “We are delighted to announce Rabbit’s expansion into the Kingdom. We pride ourselves on being a hyperlocal company, bringing our bleeding-edge tech and experience to transform the grocery shopping experience for Saudi households, and delivering the best products – especially local favorites, in just 20 minutes”.
The company’s growth strategy avoids the pitfalls of over-reliance on aggressive discounting. Instead, Rabbit leans on operational efficiency, customer retention, and smart scaling. The approach is paying off, having already attracted major investment from the likes of Lorax Capital Partners, Global Ventures, Raed Ventures, and Beltone Venture Capital, alongside earlier investors such as Global Founders Capital, Goodwater Capital, and Hub71.