News
Abu Dhabi-Backed Tech Sculpture To Be Installed In Houston
Created for the LAGI 2019 design competition in Abu Dhabi, the high-tech installation will double as a renewable power plant.
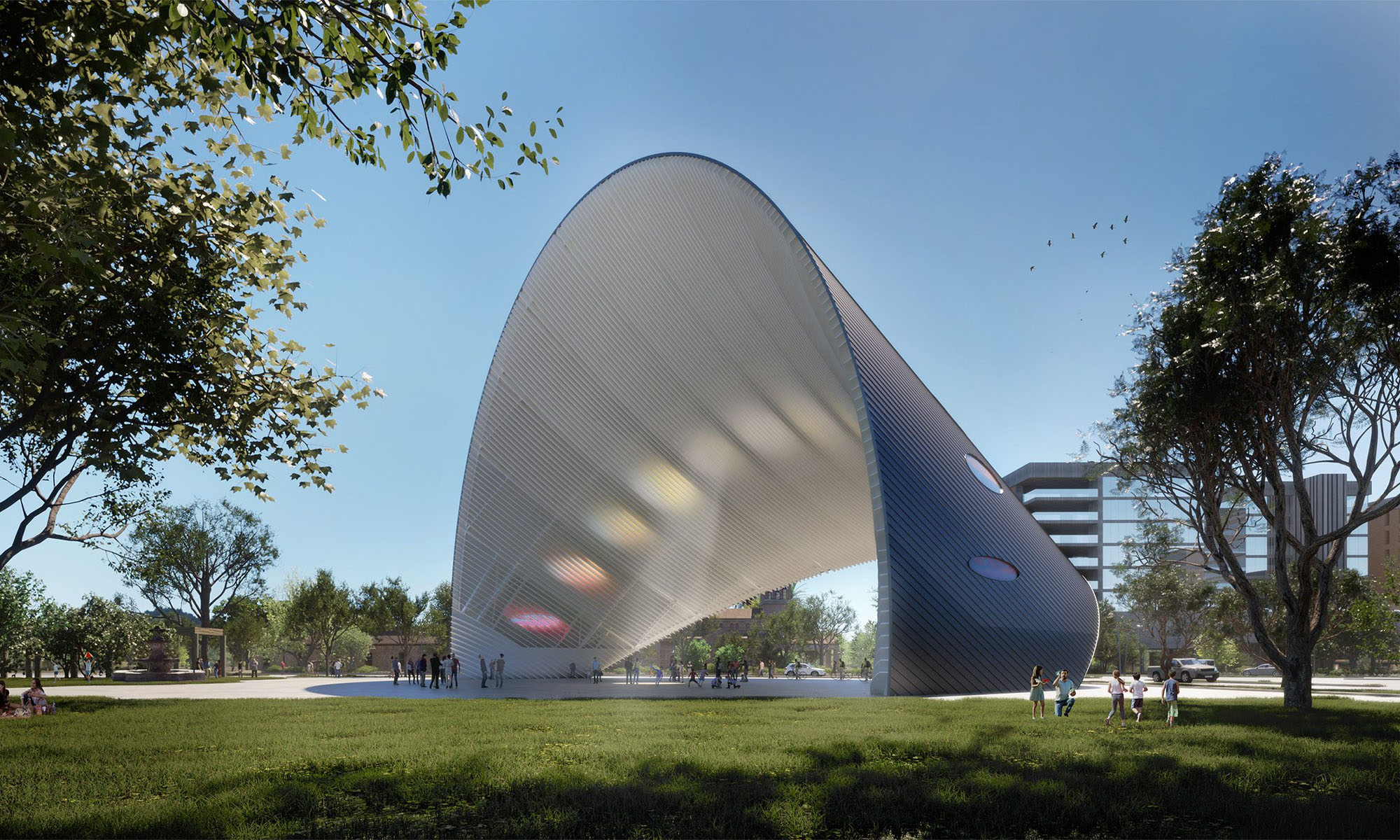

“The world’s largest sundial”, designed by Berlin architect Riccardo Mariano, is set to be installed in the city of Houston, Texas, in the city’s East End neighborhood in 2024.
The project was made possible by the Land Art Generator Initiative partnership with Masdar City, an Abu Dhabi urban development dedicated to creating sustainable cities and lifestyles. For those unaware, Houston, Texas, is twinned with the capital of the United Arab Emirates, hence the connection.
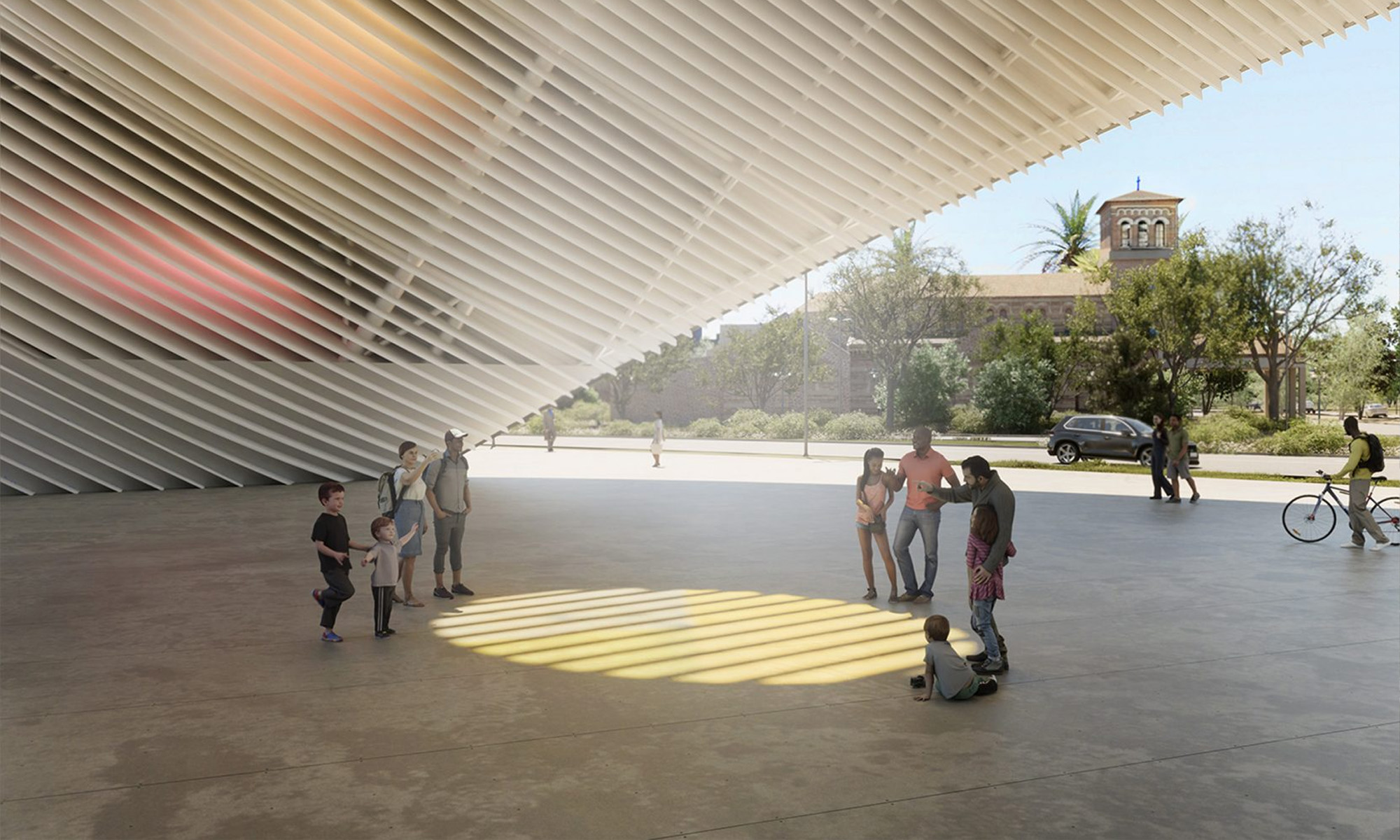

The 30-meter-tall sundial will be known as the Arco del Tiempo (Arch of Time) and functions as an interactive clock, casting sunlight onto the surface of Guadalupe Plaza Park. The installation’s geometry, carefully designed according to Houston’s latitude and longitude, is accurate throughout the seasons and hours of the day.
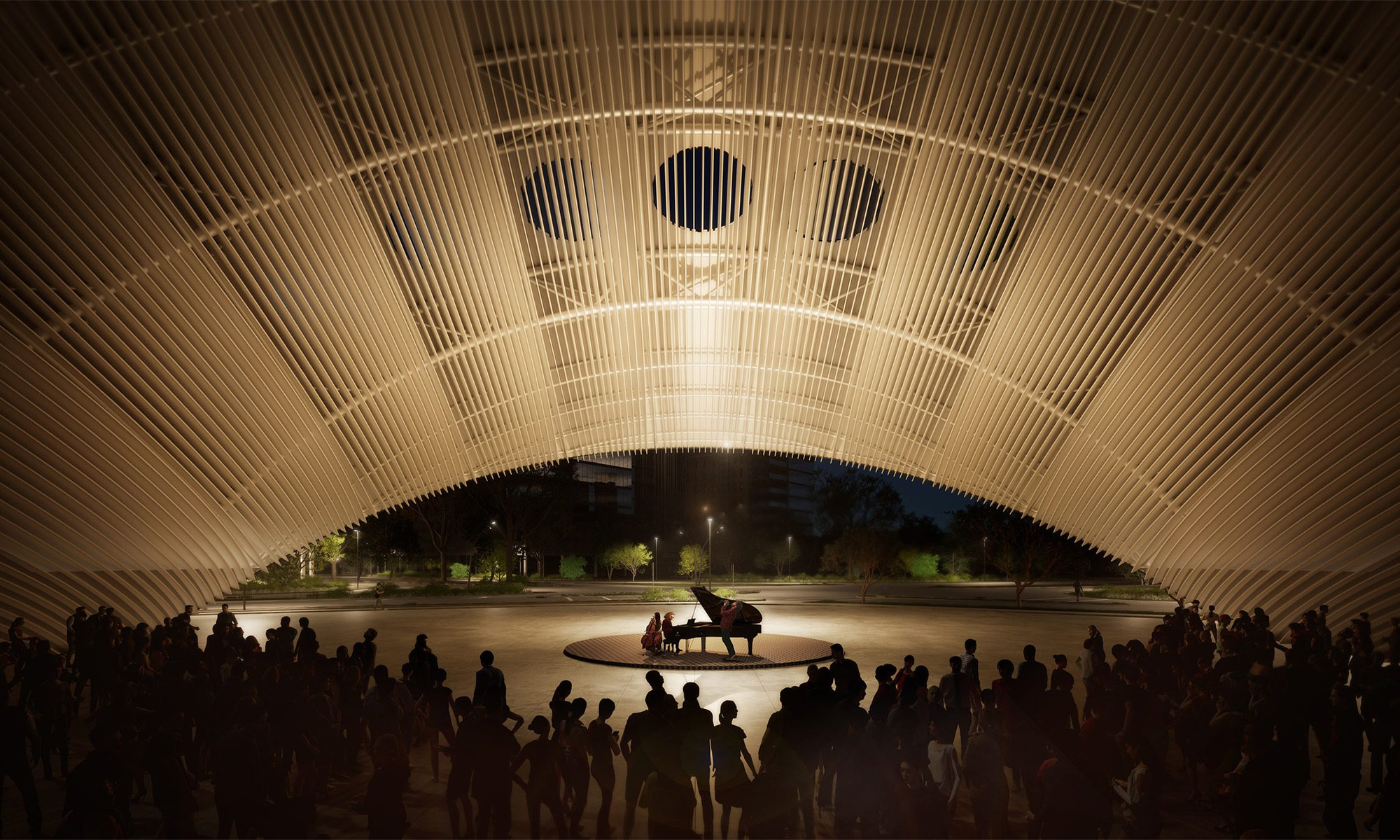

However, the Arco del Tiempo is far more than just a sculpture. The project will also serve as a renewable energy power generation plant. The finished arch will incorporate solar modules on its south-facing side, generating around 400 megawatt-hours of electricity annually — the equivalent energy consumption of 40 local homes.
Also Read: Kuwait Bans Cryptocurrencies, Putting An End To Virtual Assets
“It was a pleasure to be part of the LAGI competition in 2019, and we’re very excited to see the winning entry come to life—particularly in Abu Dhabi’s sister city,” said Chris Wan, Associate Director of Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility at Masdar City. “We know that public art plays a significant role in the fabric of a city, and Arco del Tiempo is so much more than public art: it will also educate the public about sustainability while celebrating and advocating for it. It’s a powerful combination. I hope to see more art like it in the cities of the future”.
Over its lifetime, the Arco del Tiempo is projected to generate over 12 million kilowatt-hours of renewable energy, effectively removing 8,500 metric tons of CO2.
News
Mamo Completes $3.4M Funding Round To Enhance Fintech Services
The startup will use the influx of cash to expand into Saudi Arabia and across the wider GCC while improving its product offering.

UAE-based fintech Mamo has announced the completion of a $3.4 million funding round that will help the startup extend its market presence and improve its product offering. Investors included 4DX Ventures, the Dubai Future District Fund and Cyfr Capital.
Mamo’s platform offers “payment collection, corporate cards and expense management” to help small and medium-sized businesses consolidate and streamline their operations. With the latest influx of capital, Mamo will further develop its comprehensive suite of services and begin testing its product lines in Saudi Arabia, further extending its footprint across the GCC.
Imad Gharazeddine, co-founder and CEO of Mamo, stated: “We’ve been in the market for a while now and are incredibly proud of what our team has achieved. The holistic and expansive nature of our product offering has helped us continue to grow sustainably. This additional funding will allow us to reach our medium-term goals even faster. The support from new and existing investors is a testament to our strong expertise and the ability to deliver on our customer promise”.
Daniel Marlo, General Partner of lead investor 4DX Ventures, added: “We have immense trust in Imad’s vision, leadership and Mamo’s innovative approach to provide a user-friendly and comprehensive financial solution for SMEs that makes financial management more accessible and efficient. We are proud to partner with them and support their mission”.
Also Read: A Guide To Digital Payment Methods In The Middle East
Amer Fatayer, Managing Director of Dubai Future District Fund’s investment team, also commented: “Mamo’s localized product lines serve as an infrastructure for SME payments and spend management in UAE, a segment that is underserved by the country’s current banking infrastructure. The team has taken a product-first approach to consolidating SMEs’ financial journeys and building a fintech solution deeply embedded in a business’s core operations”.
To date, Mamo has raised around $13 million in investment funding and now boasts a team of 30 people. The company’s intuitive financial services platform has allowed over 1,000 businesses to consolidate their financial operations and significantly reduce payment fees.
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoAmazon Prime Day 2024: Get Ready For 6 Days Of Amazing Deals
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoSamsung Unpacked 2024: What To Expect From The July 10 Event
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoCoursera Report Shows Surge In UAE Interest In AI Upskilling
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMeet Dubai’s Groundbreaking Smart Robot Delivery Assistant