News
Apple Announces New iPad Pro With M4 Chip And Updated iPad Air
“This is the biggest day for iPad since its introduction,” said CEO Tim Cook in a video posted to Apple’s website.
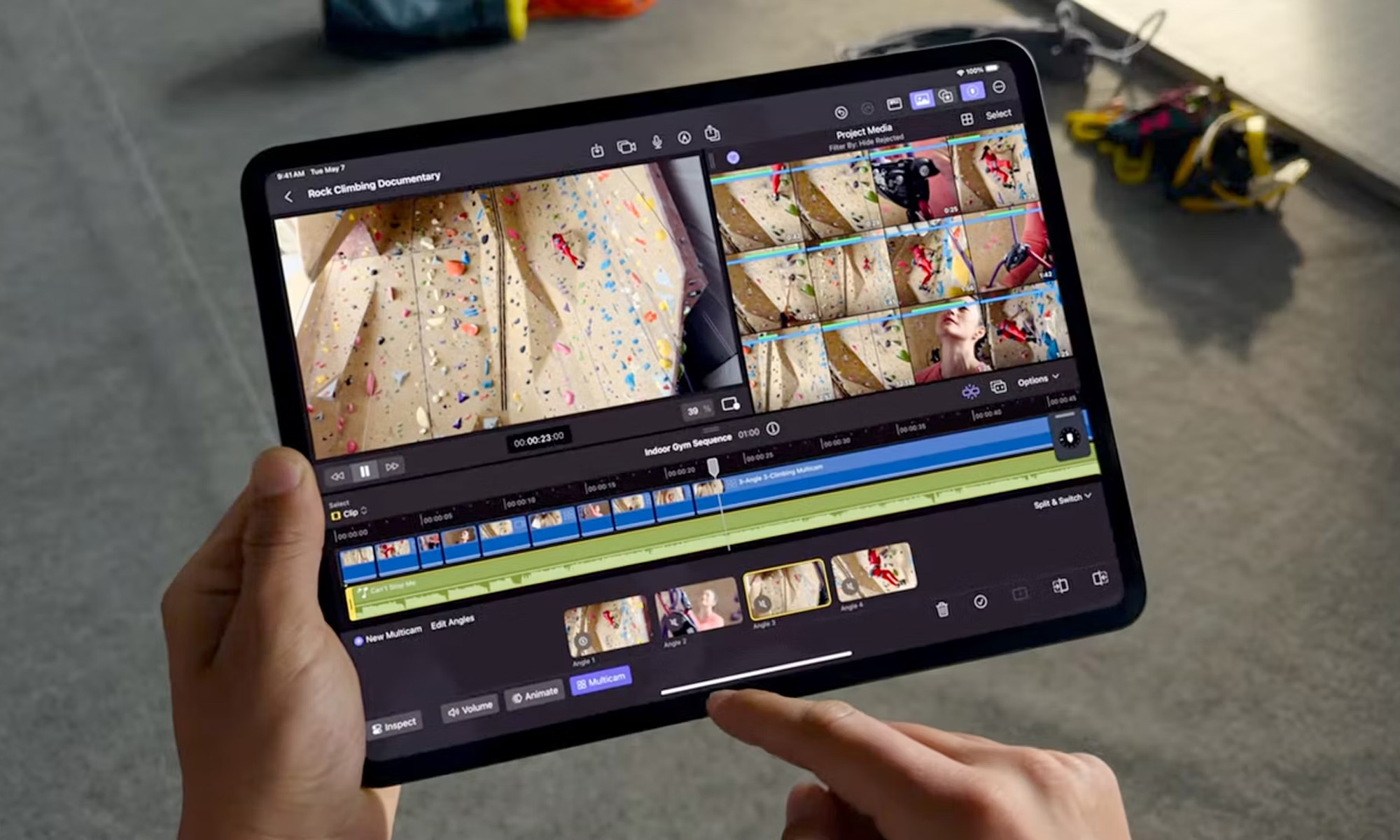
Apple’s latest updates to its popular iPad Air and Pro models were announced on Tuesday, May 7. These are the first changes since 2022, the longest stretch between new models since the iconic device was revealed in 2011.
Both the 11-inch and 12.9-inch versions of the iPad Pro have received a huge design overhaul. The most noteworthy change is the move to OLED screens, with the 12.9-inch version receiving a small bump in size to 13 inches. Apple claims the new tablets are brighter and more vibrant than outgoing models, thanks to a technology it calls “tandem OLED” or “Ultra Retina XDR”.
The 13-inch model now measures an astonishing 5.1 mm in thickness, which Apple says is its slimmest device ever. (The 11-inch version is 5.3 mm thick.) For those who prefer the look of a matte display, a nano-texture coating will also be available for the first time on the Pro models.
Finally, the new iPad Pros have received a processor bump to the latest M4 chip, which Apple says is an “outrageously powerful chip for AI”, offering an example of its ability to quickly and efficiently isolate subjects from backgrounds in videos.
The iPad Pro 11-inch starts at $999, and the larger 13-inch version starts at $1,299 with 256GB of storage.
Updated iPad Air In Two Sizes
The sixth-generation iPad Air didn’t receive as many upgrades as the iPad Pro but significantly does now come in two sizes. As with the Pro models, buyers now have the choice between an 11-inch and 13-inch screen, meaning they don’t need to invest in a Pro version just to get a 30% bump in display size.
Apple kept the same design for the iPad Air that it first revealed in 2020, complete with a USB-C port and Touch ID in the top button. The only difference is the front camera placement, which has been moved to the center of the iPad when in landscape orientation.
The 11-inch iPad Air is priced at $599 for the entry-level model, while the 13-inch version starts at $799.
Also Read: How To Clean Your Apple Watch Like A Pro
New Magic Keyboard Case
Apple also announced an updated (thinner, lighter) Magic Keyboard for its Pro iPads. The refreshed version now includes a function row (with controls for screen brightness). An aluminum palm rest and large trackpad with haptic feedback also help the premium case feel more like a Macbook.
The new Magic Keyboard is available for both the 11-inch and 13-inch iPad Pros and will be priced at $299 or $349, respectively.
Apple Pencil Pro
Apple also announced a new Apple Pencil, named Pro, at its event. The new model looks exactly the same but adds a “squeeze” function that opens a new tool palette. Meanwhile, a built-in gyroscope sensor lets you alter the orientation of the tools you’re using as you twist the device, offering finer control. Finally, the new pencil gets support for Apple’s Find My network, which should keep minds at rest at the prospect of losing the $129 device.
Finally, to round off Apple’s series of announcements, the entry-level iPad was reduced to $349 — a $100 price cut.
News
Mamo Completes $3.4M Funding Round To Enhance Fintech Services
The startup will use the influx of cash to expand into Saudi Arabia and across the wider GCC while improving its product offering.
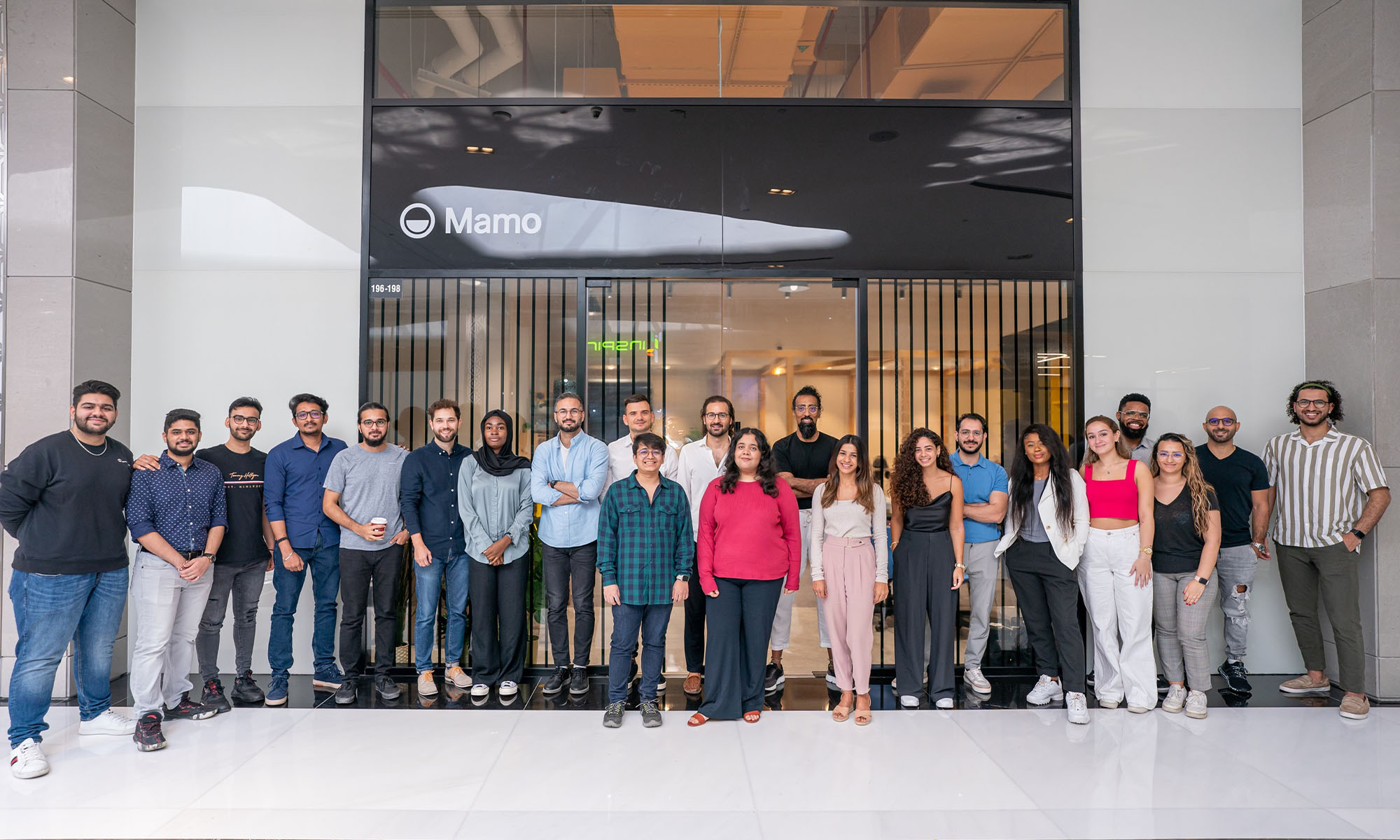

UAE-based fintech Mamo has announced the completion of a $3.4 million funding round that will help the startup extend its market presence and improve its product offering. Investors included 4DX Ventures, the Dubai Future District Fund and Cyfr Capital.
Mamo’s platform offers “payment collection, corporate cards and expense management” to help small and medium-sized businesses consolidate and streamline their operations. With the latest influx of capital, Mamo will further develop its comprehensive suite of services and begin testing its product lines in Saudi Arabia, further extending its footprint across the GCC.
Imad Gharazeddine, co-founder and CEO of Mamo, stated: “We’ve been in the market for a while now and are incredibly proud of what our team has achieved. The holistic and expansive nature of our product offering has helped us continue to grow sustainably. This additional funding will allow us to reach our medium-term goals even faster. The support from new and existing investors is a testament to our strong expertise and the ability to deliver on our customer promise”.
Daniel Marlo, General Partner of lead investor 4DX Ventures, added: “We have immense trust in Imad’s vision, leadership and Mamo’s innovative approach to provide a user-friendly and comprehensive financial solution for SMEs that makes financial management more accessible and efficient. We are proud to partner with them and support their mission”.
Also Read: A Guide To Digital Payment Methods In The Middle East
Amer Fatayer, Managing Director of Dubai Future District Fund’s investment team, also commented: “Mamo’s localized product lines serve as an infrastructure for SME payments and spend management in UAE, a segment that is underserved by the country’s current banking infrastructure. The team has taken a product-first approach to consolidating SMEs’ financial journeys and building a fintech solution deeply embedded in a business’s core operations”.
To date, Mamo has raised around $13 million in investment funding and now boasts a team of 30 people. The company’s intuitive financial services platform has allowed over 1,000 businesses to consolidate their financial operations and significantly reduce payment fees.
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoAmazon Prime Day 2024: Get Ready For 6 Days Of Amazing Deals
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoSamsung Unpacked 2024: What To Expect From The July 10 Event
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoCoursera Report Shows Surge In UAE Interest In AI Upskilling
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMeet Dubai’s Groundbreaking Smart Robot Delivery Assistant