News
Passwords Are No Longer Required To Sign Into Google Accounts
Google will allow users to replace passwords and 2FA with passkeys.
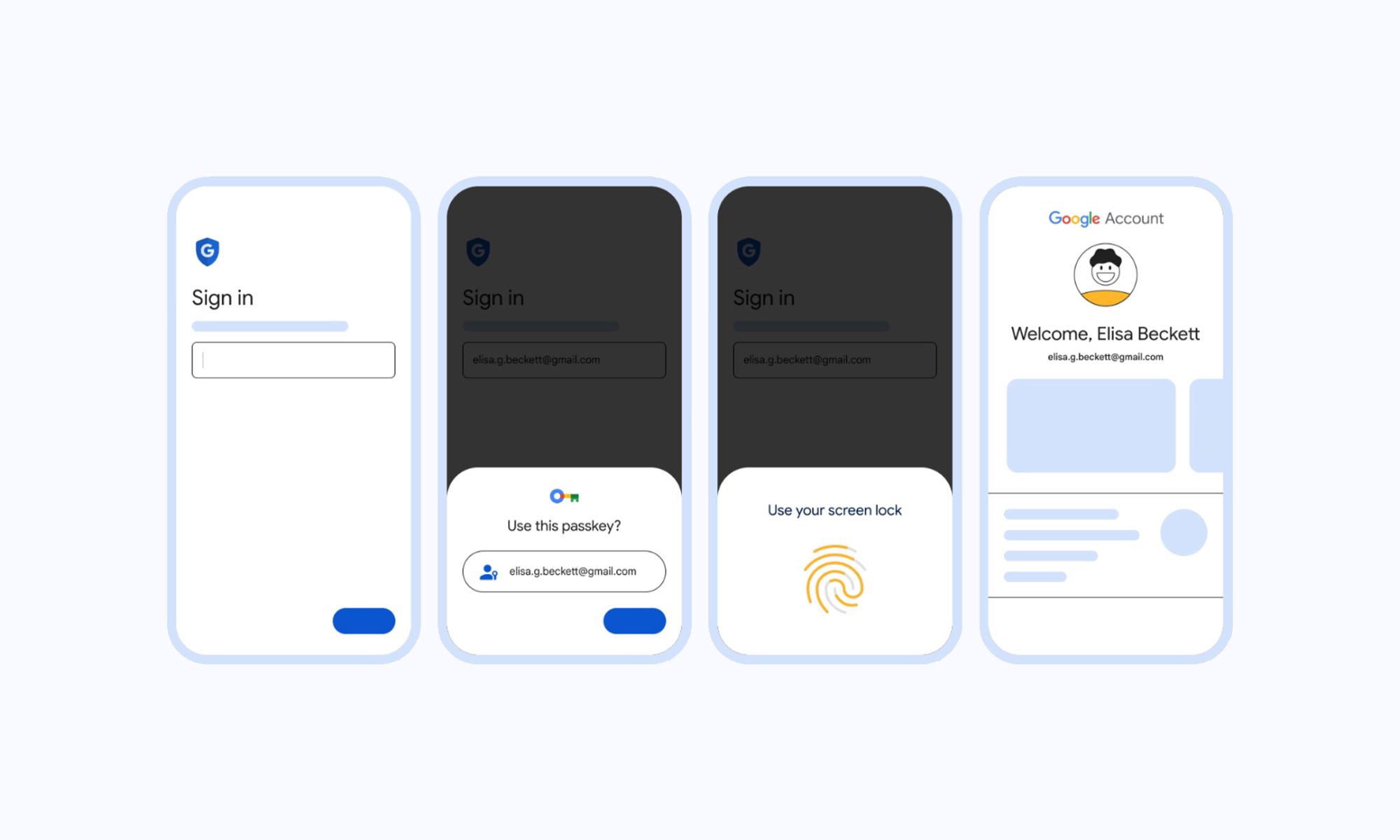
Google has taken a step towards a passwordless future, announcing that passkey functionality is being added to all Google accounts.
Passkeys are cryptographic tools that allow users to ditch passwords and two-factor verification when signing in. Google, along with Apple and Microsoft, are keen to push the technology, which uses a local PIN or a device’s biometric tools such as fingerprint scanners or Face ID.
Biometric data from passkeys isn’t shared with third parties and only exists on a user’s device, providing enhanced security since no passwords can be hacked or stolen.
When a passkey is added to a Google account, users will be prompted for it on new sign-ins or when potentially suspicious activity is detected. Passkeys can be stored on any compatible hardware, including iPhones with iOS 16 and Android devices running Android 9 and above. Users can access passkeys on other devices by using services such as iCloud or password managers like 1Password. In addition, Google also allows the following:
- Accounts can be accessed temporarily using someone else’s device by selecting “use a passkey from another device” to create a one-time sign-in.
- Passkeys can be revoked immediately in the account settings section if a user suspects a security breach, or a device is lost or stolen.
- Users of Google’s Advanced Protection Program (a free service providing additional security against phishing and malware) can use passkeys instead of physical security keys.
Also Read: Abu Dhabi Scientists Create Electronic Appetite Regulation Pill
If you’d prefer to log in to your account the traditional way, Google will continue to support regular passwords for the foreseeable future, allowing users without a biometric device to make the change once they eventually upgrade their hardware.
News
HiFuture Wraps Up Successful GITEX GLOBAL 2024 Appearance
The electronics company wowed audiences at the world’s largest tech event with a range of wearable and smart audio devices.
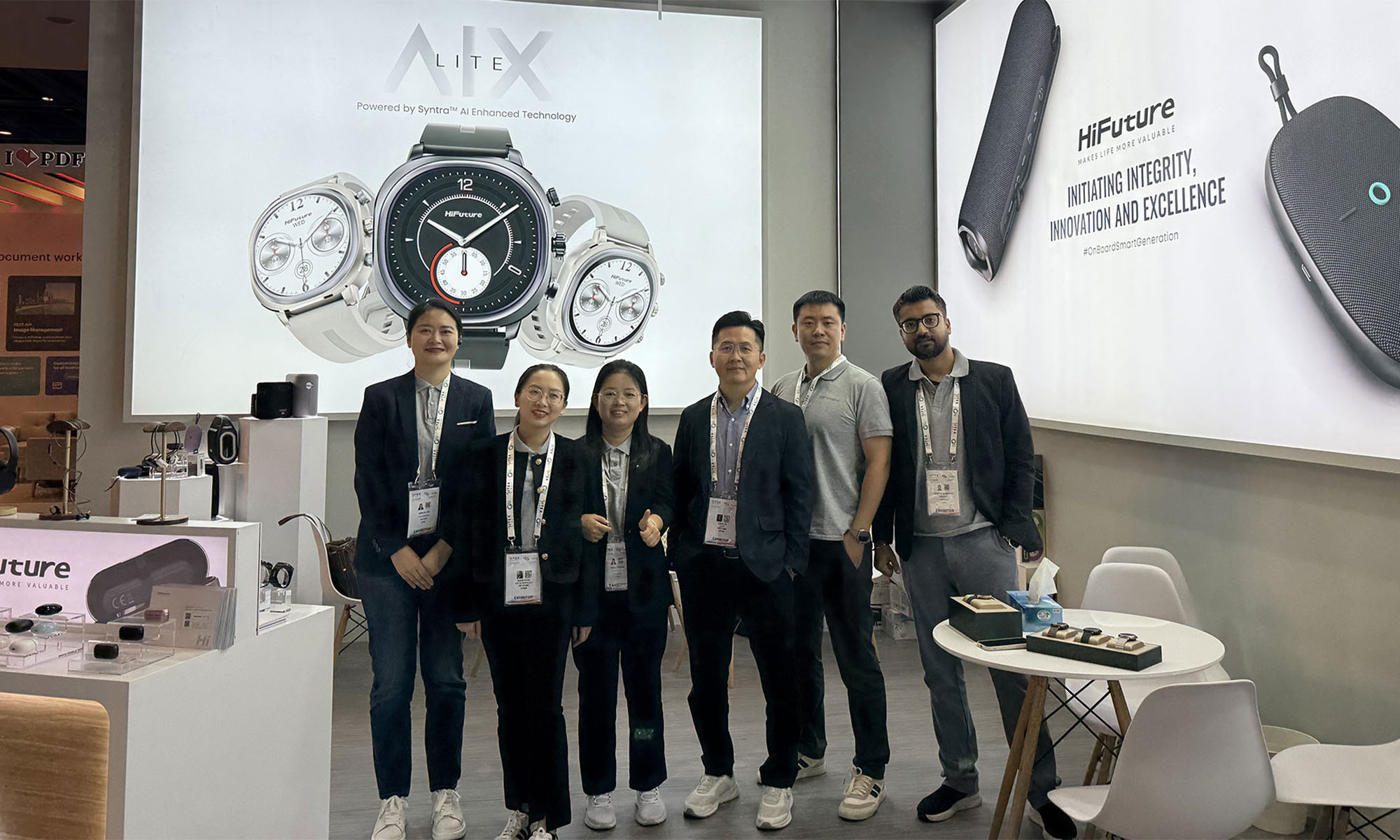

This year’s GITEX GLOBAL 2024 in Dubai saw a huge number of startups, electronics firms, and innovators from around the globe gather for the tech sector’s largest event of its kind. One company making waves at this year’s expo was Chinese tech group HiFuture, which showcased a range of products with a focus on wearable technology and smart audio.
At the HiFuture booth, the company captivated attendees with cutting-edge smartwatches like the ACTIVE and AURORA, along with a range of powerful wireless speakers, earbuds, and even smart rings. Visitors were eager to check out the sleek new designs on offer and even had the chance to test out some of the products themselves.

Among the highlights were smartwatches combining dual-core processors with customizable options. The devices blended style and technology, offering health monitoring capabilities, personalized watch faces, and advanced AI-driven functionalities, giving attendees a taste of the future of wearable technology.
On the audio front, HiFuture’s wireless speakers left a lasting impression, offering rich, immersive sound in compact, portable designs. These speakers cater to both intimate gatherings and larger celebrations, offering versatility for users. Meanwhile, the company also showed off its Syntra AI technology, which it claims “revolutionizes health and fitness tracking by combining advanced optical sensors with intelligent algorithms for precise, real-time insights”.
Also Read: How (And Why) To Start A Tech Business In Dubai
The presence of HiFuture’s leadership team at GITEX 2024 underscored the importance of this event for the company, with CEO Levin Liu leading a team of executives, all keen to engage with attendees and offer insights into HiFuture’s vision, product development process, and future direction.
Overall, it seems that GITEX GLOBAL 2024 has been a rewarding experience for HiFuture. The enthusiasm and curiosity of attendees shown to the company’s diverse range of products was obvious, with the HiFuture team leaving on a high note and clearly excited and motivated by the event.