News
Data Of 700 Million LinkedIn Users Is For Sale On The Dark Web
Who would pay for this information, you wonder? Spammers, phishers, and other cybercriminals are definitely the target audience here.

The security team at LinkedIn doesn’t get much rest lately. In April, 500 million of its user’s data was exposed by hackers, and the same data collection technique was apparently used by a dark web user called TomLiner, who is currently selling 700 million LinkedIn user records (92% of all LinkedIn users) in a convenient bundle for just $5,000.
The data collection technique in question is called scraping, which is the act of extracting useful information from a website. Since any public website can be scraped using readily available tools, it wouldn’t be correct to call this incident a breach, as LinkedIn quickly pointed out.
“While we’re still investigating this issue, our initial analysis indicates that the dataset includes information scraped from LinkedIn as well as information obtained from other sources,” said Leonna Spilman, Corporate Communications Manager at LinkedIn. “This was not a LinkedIn data breach, and our investigation has determined that no private LinkedIn member data was exposed.”
So, what data has been exposed? Fortunately, no passwords or dates of birth. Here’s what a sample of one million records published by the scrapper contains:
- Email addresses
- Full names
- Phone numbers
- Physical addresses
- Geolocation records
- LinkedIn username and profile URL
- Personal and professional experience/background
- Genders
- Other social media accounts and usernames
Who would pay $5,000 for this information, you wonder? Spammers, phishers, and other cybercriminals are definitely the target audience here.
Also Read: Is Your Phone Hacked? How To Find Out & Protect Yourself
Having all this information in one place makes it much easier for them to create detailed profiles of their potential victims and launch sophisticated targeted attacks against them. Sure, they could simply scape it by themselves using LinkedIn’s own API (application program interface) just like the seller did, but cybercrime can be so profitable that their time is often more valuable.
If you have a LinkedIn account, then you should assume that your personal information is included in the dataset and act accordingly. More specifically, you should enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and avoid replying to email messages from unknown senders, let alone opening any attachments they may contain.
News
HiFuture Wraps Up Successful GITEX GLOBAL 2024 Appearance
The electronics company wowed audiences at the world’s largest tech event with a range of wearable and smart audio devices.
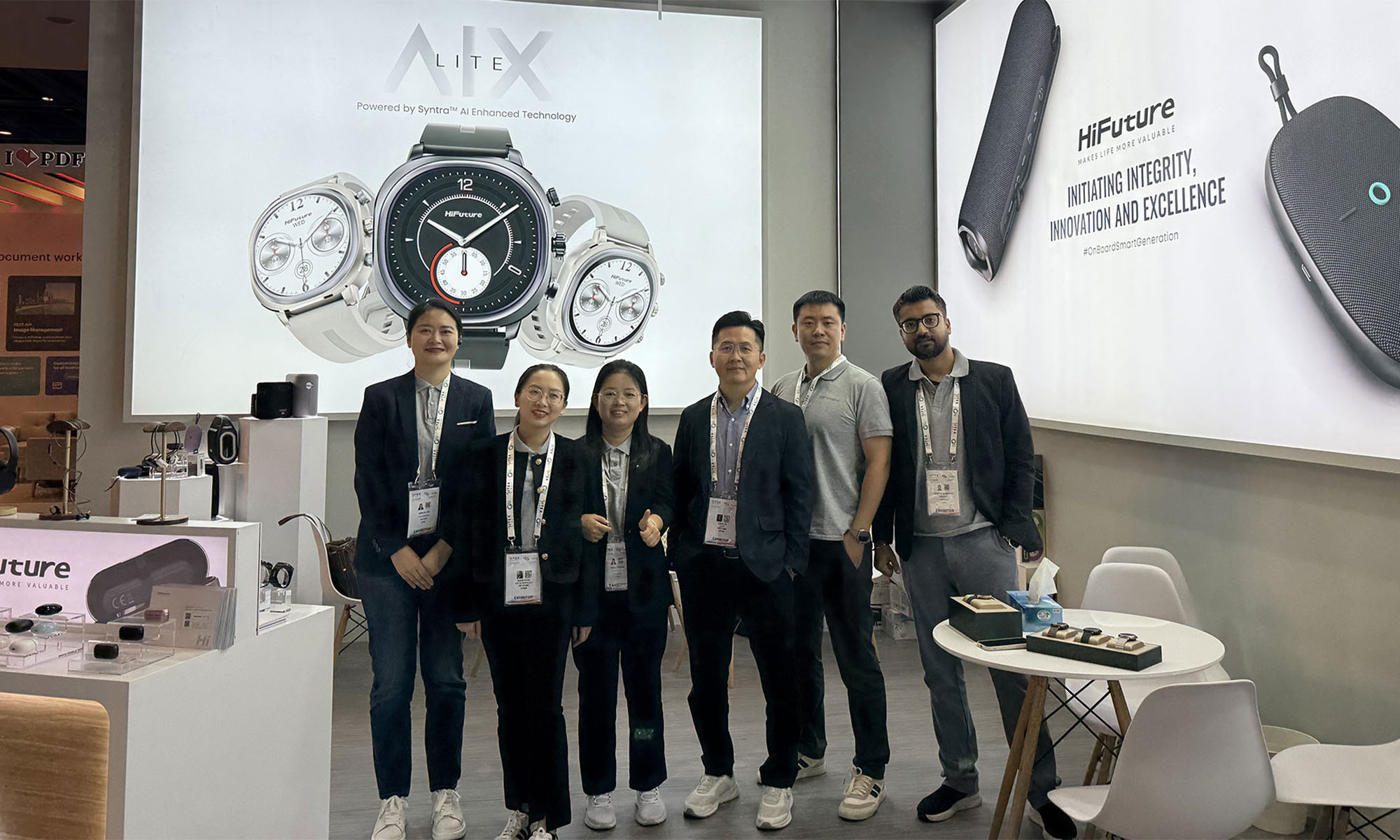

This year’s GITEX GLOBAL 2024 in Dubai saw a huge number of startups, electronics firms, and innovators from around the globe gather for the tech sector’s largest event of its kind. One company making waves at this year’s expo was Chinese tech group HiFuture, which showcased a range of products with a focus on wearable technology and smart audio.
At the HiFuture booth, the company captivated attendees with cutting-edge smartwatches like the ACTIVE and AURORA, along with a range of powerful wireless speakers, earbuds, and even smart rings. Visitors were eager to check out the sleek new designs on offer and even had the chance to test out some of the products themselves.

Among the highlights were smartwatches combining dual-core processors with customizable options. The devices blended style and technology, offering health monitoring capabilities, personalized watch faces, and advanced AI-driven functionalities, giving attendees a taste of the future of wearable technology.
On the audio front, HiFuture’s wireless speakers left a lasting impression, offering rich, immersive sound in compact, portable designs. These speakers cater to both intimate gatherings and larger celebrations, offering versatility for users. Meanwhile, the company also showed off its Syntra AI technology, which it claims “revolutionizes health and fitness tracking by combining advanced optical sensors with intelligent algorithms for precise, real-time insights”.
Also Read: How (And Why) To Start A Tech Business In Dubai
The presence of HiFuture’s leadership team at GITEX 2024 underscored the importance of this event for the company, with CEO Levin Liu leading a team of executives, all keen to engage with attendees and offer insights into HiFuture’s vision, product development process, and future direction.
Overall, it seems that GITEX GLOBAL 2024 has been a rewarding experience for HiFuture. The enthusiasm and curiosity of attendees shown to the company’s diverse range of products was obvious, with the HiFuture team leaving on a high note and clearly excited and motivated by the event.