News
Google Brings Plus Codes To 18 MENA Countries
The geocode system behind the feature, called the Open Location Code, was developed at Google’s Zürich engineering office and launched in 2014.
The Plus Codes feature of Google Maps will soon be turned on for users in 18 MENA countries, including Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Egypt, Morocco, and Algeria.
The feature allows Google Maps users to turn their latitude and longitude co-ordinates into a short sequence of numbers and letters that they can easily share with others.
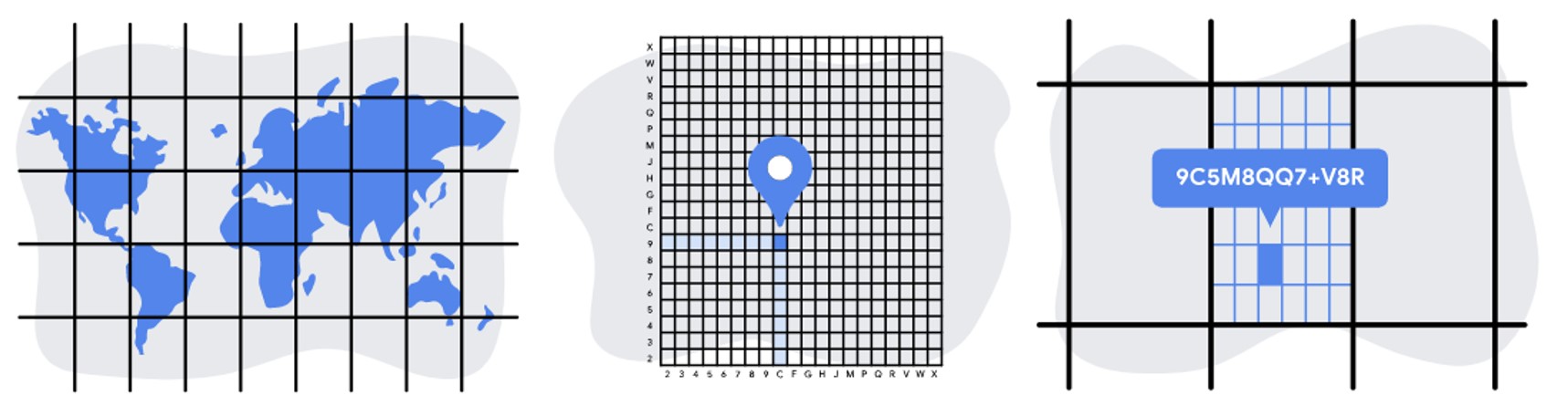
“Plus Codes are like street addresses for people or places that don’t have one,” explains Google. “With a Plus Code, people can receive deliveries, access emergency and social services, or just help other people find them.”
The geocode system behind the feature, called the Open Location Code (OLC), was developed at Google’s Zürich engineering office and launched in 2014.
Also Read: Disney+ Confirms Its Middle East Launch Date
Earlier this year, Plus Codes launched in India, quickly attracting hundreds of thousands of users. Plus Codes are also widely used by non-governmental organizations (NGOs), governments in Sub-Saharan Africa, and businesses that want to make it easier for customers to find them.
To Generate A Plus Code On A Computer
- Open Google Maps.
- Select the location for which you want to generate a Plus Code.
- Click the coordinates (such as 49.475019, 17.116156) displayed in the info box at the bottom.
- Hover your mouse over the plus code in the left pane.
- Click the copy button to copy the generated Plus Code to the clipboard.
To Generate A Plus Code On A Mobile Device
- Launch the Google Maps app.
- Drop a pin at the location for which you want to generate a Plus Code.
- Tap the “Dropped pin” panel at the bottom.
- Find the Plus Code beside the Plus Code logo.
- Tap the Plus Code to copy it to the clipboard.
Alternatively, you can use the map on the official website of Plus Code to quickly generate a Plus Code for any location with a street address.
News
HiFuture Wraps Up Successful GITEX GLOBAL 2024 Appearance
The electronics company wowed audiences at the world’s largest tech event with a range of wearable and smart audio devices.
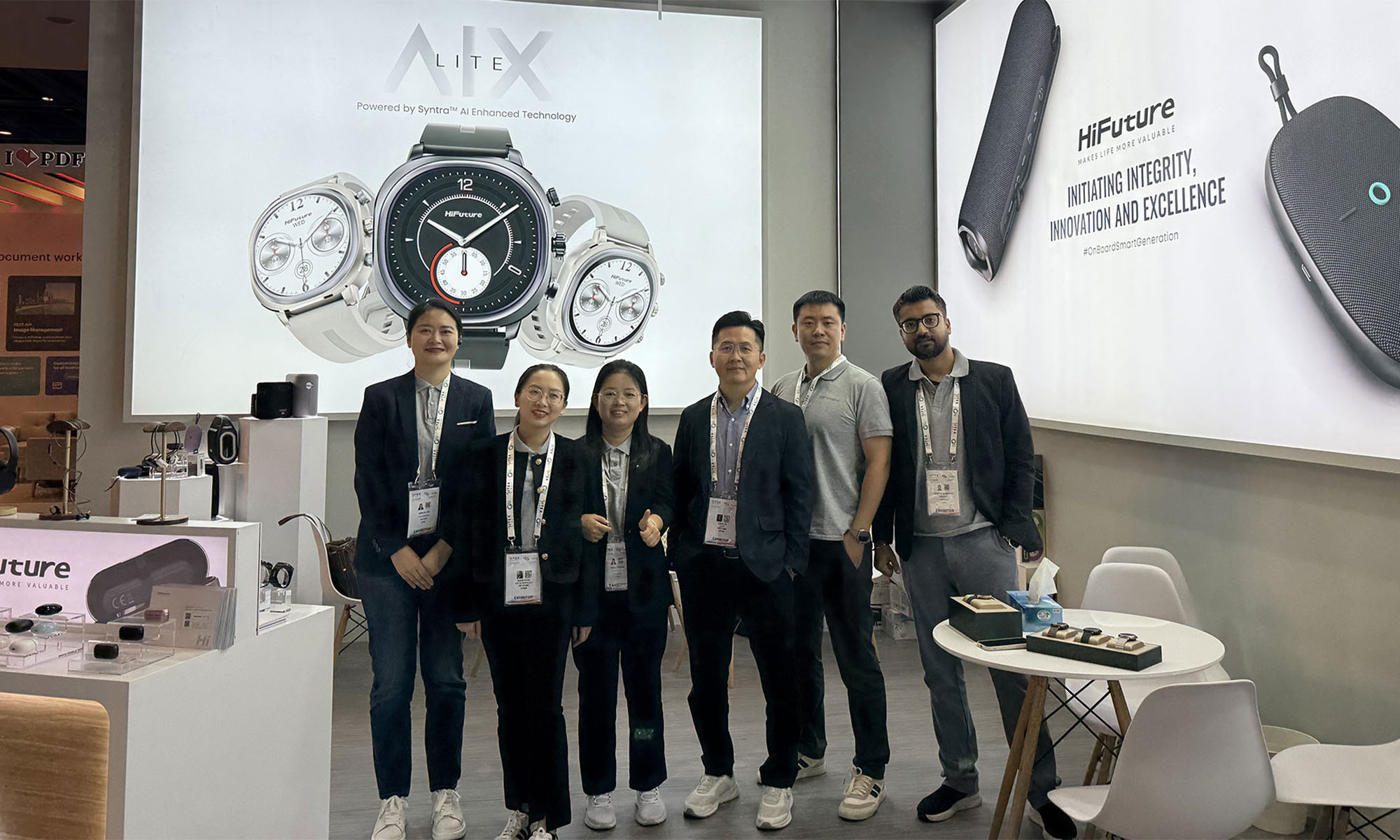

This year’s GITEX GLOBAL 2024 in Dubai saw a huge number of startups, electronics firms, and innovators from around the globe gather for the tech sector’s largest event of its kind. One company making waves at this year’s expo was Chinese tech group HiFuture, which showcased a range of products with a focus on wearable technology and smart audio.
At the HiFuture booth, the company captivated attendees with cutting-edge smartwatches like the ACTIVE and AURORA, along with a range of powerful wireless speakers, earbuds, and even smart rings. Visitors were eager to check out the sleek new designs on offer and even had the chance to test out some of the products themselves.

Among the highlights were smartwatches combining dual-core processors with customizable options. The devices blended style and technology, offering health monitoring capabilities, personalized watch faces, and advanced AI-driven functionalities, giving attendees a taste of the future of wearable technology.
On the audio front, HiFuture’s wireless speakers left a lasting impression, offering rich, immersive sound in compact, portable designs. These speakers cater to both intimate gatherings and larger celebrations, offering versatility for users. Meanwhile, the company also showed off its Syntra AI technology, which it claims “revolutionizes health and fitness tracking by combining advanced optical sensors with intelligent algorithms for precise, real-time insights”.
Also Read: How (And Why) To Start A Tech Business In Dubai
The presence of HiFuture’s leadership team at GITEX 2024 underscored the importance of this event for the company, with CEO Levin Liu leading a team of executives, all keen to engage with attendees and offer insights into HiFuture’s vision, product development process, and future direction.
Overall, it seems that GITEX GLOBAL 2024 has been a rewarding experience for HiFuture. The enthusiasm and curiosity of attendees shown to the company’s diverse range of products was obvious, with the HiFuture team leaving on a high note and clearly excited and motivated by the event.