News
Google Chrome Exploit Results In Attack On Lebanese Journalists
According to antivirus company Avast, there is evidence that an Israeli spyware firm called Candiru used a vulnerability in Google Chrome to spy on journalists in Lebanon.

In early July 2022, Google patched a previously unknown vulnerability in its Chrome browser, known as CVE-2022-2294. The zero-day Chrome exploit only came to light after it was apparently used to spy on journalists in Lebanon.
Antivirus company, Avast, collated a report, which it delivered to Google detailing the zero-day exploit. In this report, Avast claims that Israeli spyware firm, Candiru, used the exploit to install spyware on the journalist’s computers.
It equally believes that the firm has used similar exploits to target Avast users in Turkey, Lebanon, Palestine and Yemen beginning in March of this year.
A zero-day exploit is, in short, a vulnerability in a piece of software that is unknown to the developers. They are typically discovered in the wild for this reason, and are known as zero-day because the developers have zero days in which to address the issue. This is because the vulnerability has the potential to cause damage from the moment it is discovered.
Avast alleges that Candiru used the above-mentioned exploit to gain access to user’s computers. It is believed to have compromised a website, which it used to redirect users to a server that could collect their data. If the data – collected on 50 data points such as location, language, time zone, etc. – met their requirements, the server would establish an encrypted channel.
Despite not claiming responsibility, Candiru is the prime suspect in the attack because the CVE-2022-2294 exploit was used to install the DevilsTongue spyware. This is a piece of malware previously linked to the group by Microsoft in a separate string of attacks.
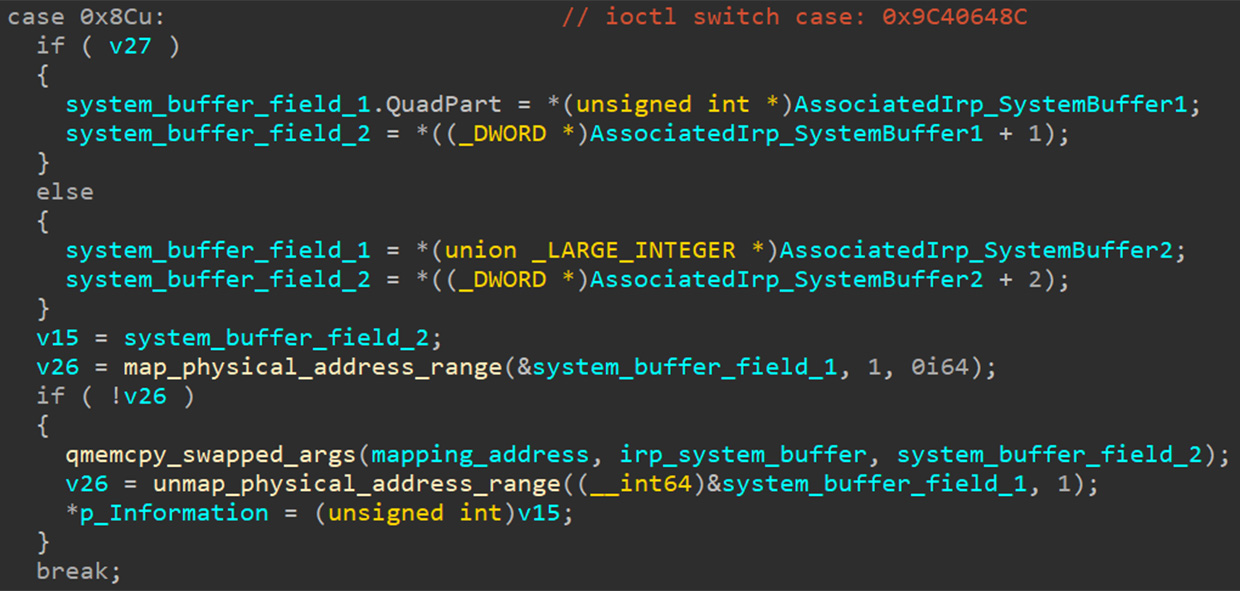
In its report, Avast claims that the zero-day exploit was used alongside another vulnerability capable of bypassing the sandbox security function in Chromium. However, Avast has (as yet) been unable to determine the second exploit used by the alleged attackers.
Also Read: DDoS Attacks Are A Growing Threat In Gaming
Luckily, Google released a patch for the exploit on July 4. As such, there is no need for Chrome users to be concerned, providing browsers are kept up to date. Microsoft and Apple have released patches for their Edge and Safari browsers, too, as they also use WebRTC.
Candiru has not yet been officially connected to the incident, so its involvement is currently (albeit well-informed) speculation. However, the tools used and computers targeted matches its previous spyware attempts dating from 2021 and early 2022. As the company has no public online presence, this fact is unlikely to change anytime soon.
News
Rabbit Expands Hyperlocal Delivery Service In Saudi Arabia
The e-commerce startup is aiming to tap into the Kingdom’s underdeveloped e-grocery sector with a tech-first, locally rooted strategy.
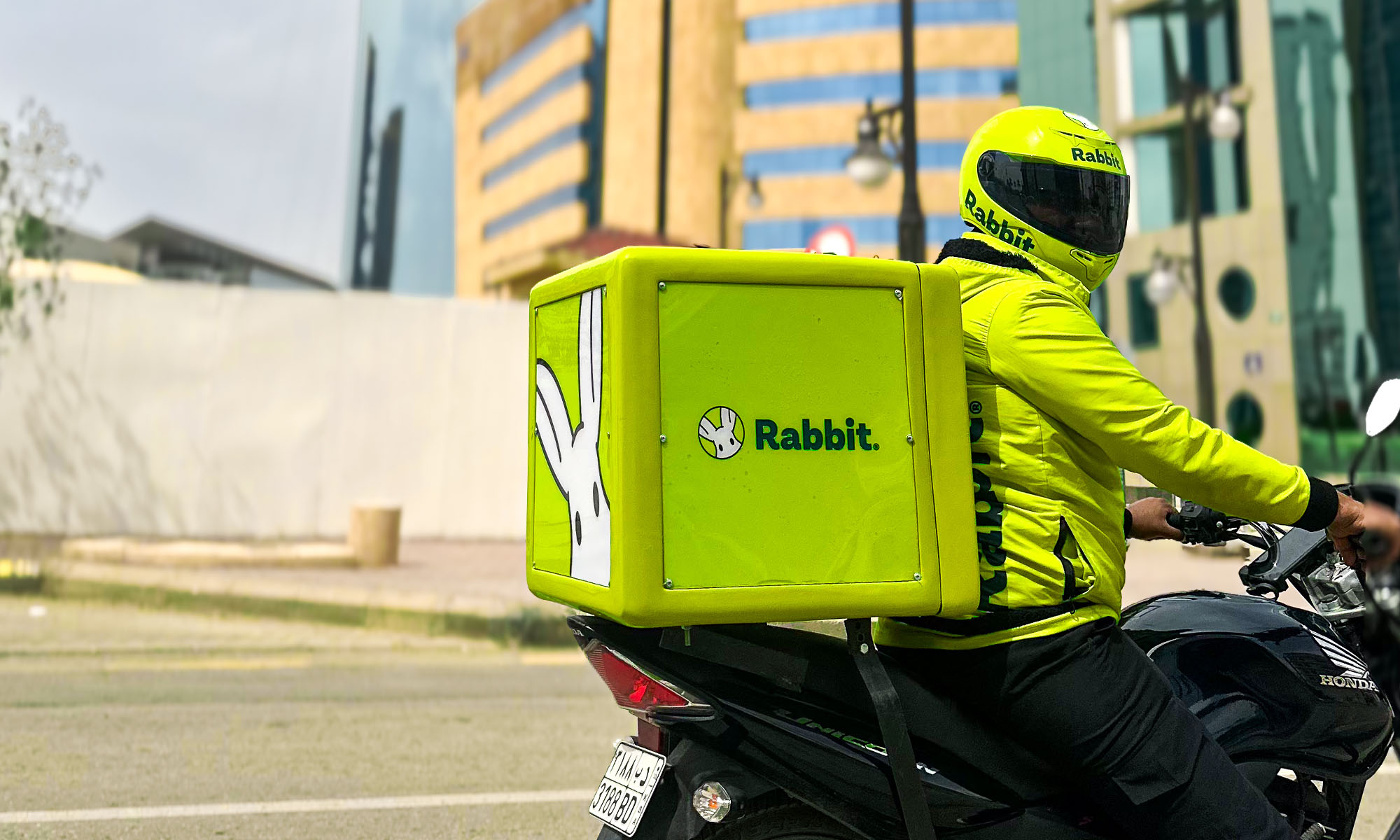

Rabbit, an Egyptian-born hyperlocal e-commerce startup, is expanding into the Saudi Arabian market, setting its sights on delivering 20 million items across major cities by 2026.
The company, founded in 2021, is already operational in the Kingdom, with its regional headquarters now open in Riyadh and an established network of strategically located fulfillment centers — commonly known as “dark stores” — across the capital.
The timing is strategic: Saudi Arabia’s online grocery transactions currently sit at 1.3%, notably behind the UAE (5.3%) and the United States (4.8%). With the Kingdom’s food and grocery market estimated at $60 billion, even a modest increase in online adoption could create a multi-billion-dollar opportunity.
Rabbit also sees a clear alignment between its business goals and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, which aims to boost retail sector innovation, support small and medium-sized enterprises, attract foreign investment, and develop a robust digital economy.
The company’s e-commerce model is based on speed and efficiency. Delivery of anything from groceries and snacks to cosmetics and household staples is promised in 20 minutes or less, facilitated by a tightly optimized logistics system — a crucial component in a sector where profit margins and delivery expectations are razor-thin.
Despite the challenges, Rabbit has already found its stride in Egypt. In just over three years, the app has been used by 1.4 million customers to deliver more than 40 million items. Revenue has surged, growing more than eightfold in the past two years alone.
Also Read: Top E-Commerce Websites In The Middle East In 2025
CEO and Co-Founder Ahmad Yousry commented: “We are delighted to announce Rabbit’s expansion into the Kingdom. We pride ourselves on being a hyperlocal company, bringing our bleeding-edge tech and experience to transform the grocery shopping experience for Saudi households, and delivering the best products – especially local favorites, in just 20 minutes”.
The company’s growth strategy avoids the pitfalls of over-reliance on aggressive discounting. Instead, Rabbit leans on operational efficiency, customer retention, and smart scaling. The approach is paying off, having already attracted major investment from the likes of Lorax Capital Partners, Global Ventures, Raed Ventures, and Beltone Venture Capital, alongside earlier investors such as Global Founders Capital, Goodwater Capital, and Hub71.