News
Meet The Smart Contact Lenses Powered By Tears
Researchers in Singapore have revolutionized the humble contact lens with self-charging smart capabilities.
Contact lenses have been used to successfully correct vision for decades, but recently, they’re beginning to evolve into something much more interesting.
Researchers from the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) in Singapore have developed a tiny micrometer-thin battery that can power futuristic smart contact lenses that rely on the wearer’s tears for power.
Although smart contacts are nothing new, most attempts so far have relied on thin batteries with tiny induction coils and wires. Obviously, these metal parts aren’t ideal for a device that sits directly on the wearer’s eye, so an NTU School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE) research team led by Lee Seok Woo has been working on something better.
According to a press release, the NTU team’s battery uses biocompatible materials coated with a glucose-based layer. The coating reacts with the sodium and chloride ions present in the battery to generate electricity. Since both sodium and chloride ions are also found in tears, the smart lens battery can also be recharged while in use with no additional effort from the wearer.
Speaking about the research, Lee Seok Woo said, “This research began with a simple question: Could contact lens batteries be recharged with our tears? Previous techniques for lens batteries were imperfect, as one side of the battery electrode was charged, and the other was not. Our approach can charge both electrodes of a battery through a unique combination of enzymatic reaction and self-reduction reaction”.
Also Read: Social Media Addiction Is Greatly Impacting Arab Youth
According to the NTU team, the lenses should be good for a full day of use, and can also be placed in a special solution that keeps the battery charged. “By combining the battery and biofuel cell into a single component, the battery can charge itself without the need for additional space for wired or wireless components. Furthermore, the electrodes placed at the outer side of the smart contact lenses ensure that the eye’s vision cannot be obstructed”.
The NTU scientists are already working on boosting the amount of electricity the lens battery can deliver. Their research has been published in the journal Nano Energy, and they’re also in the process of partnering with contact lens producers to bring the technology to the market.
News
HiFuture Wraps Up Successful GITEX GLOBAL 2024 Appearance
The electronics company wowed audiences at the world’s largest tech event with a range of wearable and smart audio devices.
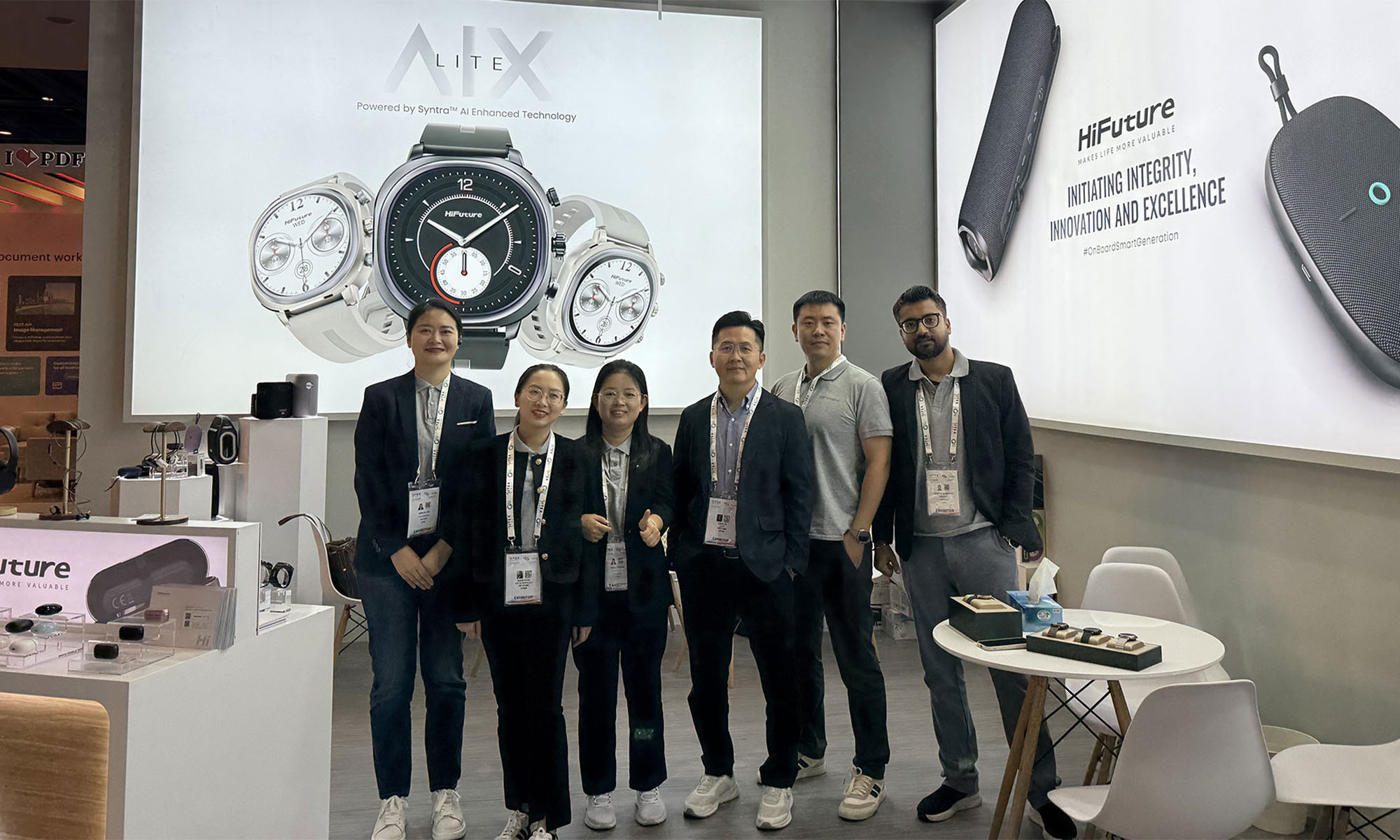

This year’s GITEX GLOBAL 2024 in Dubai saw a huge number of startups, electronics firms, and innovators from around the globe gather for the tech sector’s largest event of its kind. One company making waves at this year’s expo was Chinese tech group HiFuture, which showcased a range of products with a focus on wearable technology and smart audio.
At the HiFuture booth, the company captivated attendees with cutting-edge smartwatches like the ACTIVE and AURORA, along with a range of powerful wireless speakers, earbuds, and even smart rings. Visitors were eager to check out the sleek new designs on offer and even had the chance to test out some of the products themselves.

Among the highlights were smartwatches combining dual-core processors with customizable options. The devices blended style and technology, offering health monitoring capabilities, personalized watch faces, and advanced AI-driven functionalities, giving attendees a taste of the future of wearable technology.
On the audio front, HiFuture’s wireless speakers left a lasting impression, offering rich, immersive sound in compact, portable designs. These speakers cater to both intimate gatherings and larger celebrations, offering versatility for users. Meanwhile, the company also showed off its Syntra AI technology, which it claims “revolutionizes health and fitness tracking by combining advanced optical sensors with intelligent algorithms for precise, real-time insights”.
Also Read: How (And Why) To Start A Tech Business In Dubai
The presence of HiFuture’s leadership team at GITEX 2024 underscored the importance of this event for the company, with CEO Levin Liu leading a team of executives, all keen to engage with attendees and offer insights into HiFuture’s vision, product development process, and future direction.
Overall, it seems that GITEX GLOBAL 2024 has been a rewarding experience for HiFuture. The enthusiasm and curiosity of attendees shown to the company’s diverse range of products was obvious, with the HiFuture team leaving on a high note and clearly excited and motivated by the event.